If your engine is overheating, check for coolant leaks, low fluid levels, or damaged hoses that can hinder heat transfer. Faulty thermostats or temperature sensors may cause improper coolant circulation, while radiator blockages or a malfunctioning water pump can reduce cooling efficiency. Damaged cooling fans and heavy engine loads, like towing, also raise risks. External factors like hot weather or rough terrain worsen the problem. Keep investigating these causes—there’s more to learn to prevent damage.
Key Takeaways
- Check coolant levels regularly and inspect for leaks, cracks, or evaporation issues affecting heat transfer.
- Test the thermostat and temperature sensors for proper operation and calibration accuracy.
- Examine radiator, hoses, and cooling fans for damage, blockages, or failure that impair airflow and coolant circulation.
- Inspect the water pump and belts for signs of wear, leaks, or noise indicating potential failure.
- Consider external factors like ambient temperature, terrain, and driving conditions that increase engine load and overheating risk.
Coolant Leaks and Low Fluid Levels

One common cause of engine overheating is coolant leaks, which lead to low fluid levels. Radiator leaks are a frequent culprit, allowing coolant to escape and reducing the amount available to regulate engine temperature. Over time, coolant evaporation can also diminish fluid levels, especially if your radiator isn’t sealed properly or if there are small cracks. When coolant levels drop, the system can’t effectively absorb and dissipate heat, causing the engine to overheat. Regularly inspecting your radiator and hoses for leaks and cracks can help catch issues early. Keeping an eye on coolant levels between oil changes guarantees you’re aware of any loss. Addressing radiator leaks promptly and topping off coolant prevents overheating and protects your engine from damage. Proper maintenance and coolant system care are essential for avoiding overheating issues.
Faulty Thermostat and Temperature Sensor

A faulty thermostat can cause your engine to overheat or run too cold, often showing signs like erratic temperature readings or engine overheating warnings. If your temperature sensor isn’t calibrated correctly, it may give inaccurate readings, leading to improper cooling system responses. These issues directly impact your cooling system’s effectiveness and should be addressed promptly to prevent further damage. Implementing regular maintenance and audits of your cooling system components can help identify potential problems early and ensure optimal performance.
Thermostat Malfunction Signs
When your vehicle’s thermostat or temperature sensor malfunctions, you might notice abnormal engine temperature readings or inconsistent heater performance. A faulty thermostat can cause coolant evaporation issues, leading to overheating or engine sluggishness. You may also see signs of radiator corrosion, which impacts cooling efficiency and signals potential thermostat problems. If the thermostat sticks in the closed position, the engine quickly overheats, while a stuck-open thermostat results in the engine running too cool, affecting performance. Additionally, you might observe fluctuations in temperature gauge readings or a heater that suddenly stops working properly. These signs indicate your thermostat isn’t regulating coolant flow correctly, risking engine damage. Promptly addressing these symptoms can prevent severe overheating and costly repairs down the line.
Sensor Calibration Issues
Faulty thermostats and malfunctioning temperature sensors can cause calibration issues that lead to inaccurate engine temperature readings. When sensor calibration is off, your vehicle’s electronic system diagnostics may misinterpret engine heat levels, causing the engine control unit to make incorrect adjustments. This can result in the engine running too hot or too cold, both of which contribute to overheating risks. To identify such issues, you should perform electronic system diagnostics that specifically check sensor responses and calibration accuracy. If a sensor isn’t calibrated correctly, replacing or recalibrating it can restore accurate readings. Creativity in troubleshooting can also help identify and resolve sensor calibration problems more effectively. Regular maintenance and diagnostics help guarantee your temperature sensors are functioning properly, preventing false signals that could lead to overheating or inefficient engine performance.
Impact on Cooling System
A malfunctioning thermostat or temperature sensor can directly disrupt your cooling system’s effectiveness, leading to overheating issues. When these components fail, they may cause incorrect readings or prevent the thermostat from opening properly, which affects coolant flow. This can result in an improper coolant mixture circulating through the engine, reducing its ability to dissipate heat. Additionally, a faulty sensor might give false temperature readings, causing the cooling fan or radiator to activate at the wrong times. If the thermostat remains closed, coolant can’t reach the radiator, exceeding its capacity to cool the engine. Over time, this imbalance stresses the system, increasing overheating risks. Ensuring your thermostat and temperature sensor function correctly maintains proper coolant circulation and prevents coolant mixture issues, safeguarding your radiator’s capacity and engine health. Understanding the importance of color accuracy in engine diagnostics can also help identify subtle issues before they lead to overheating.
Radiator Blockages and Damage
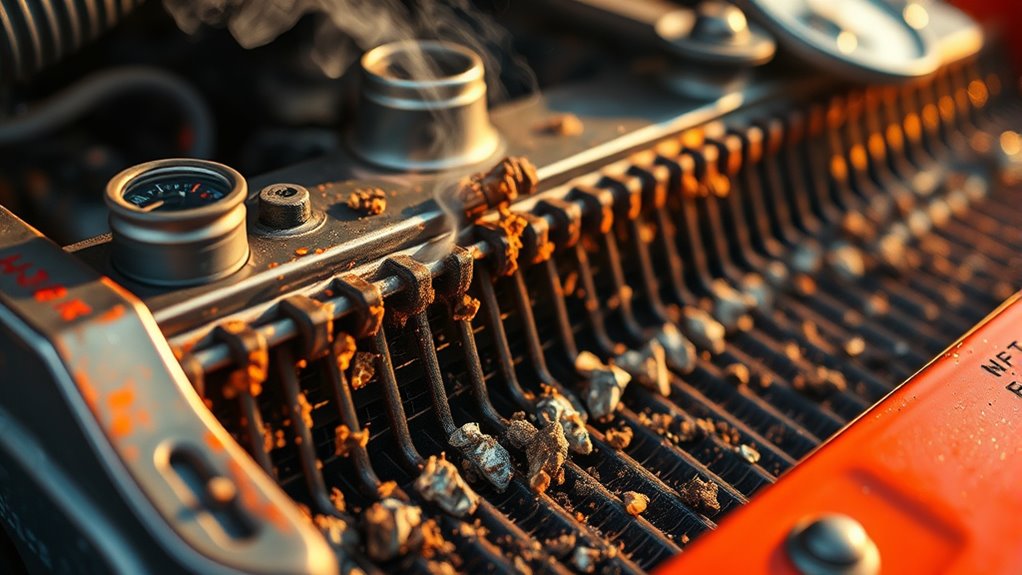

Radiator blockages and damage are common causes of engine overheating that you should investigate promptly. When your radiator is blocked, debris, rust, or sludge can restrict coolant flow, reducing heat dissipation. Damage to the radiator, such as leaks or bent fins, also impairs its ability to cool the engine effectively. Identifying these issues early prevents further engine damage and costly repairs.
- Accumulation of debris or dirt inside the radiator
- Rust or corrosion causing internal blockages
- Cracked or leaking radiator tanks
- Bent or damaged radiator fins obstructing airflow
- Disconnected or damaged radiator hoses affecting coolant flow
Water Pump Malfunctions

You might notice your engine overheating or hear squealing noises, which can indicate water pump failure. Recognizing these signs early helps prevent serious damage and costly repairs. When it’s time to replace the pump, follow proper installation tips to guarantee reliable performance. Additionally, ensuring the cooling system functions properly is crucial, as engine safety relies heavily on the water pump’s effectiveness.
Water Pump Failure Signs
Water pump failures often reveal themselves through noticeable signs that indicate it’s no longer functioning properly. You might hear unusual water pump noise, which suggests the pump’s bearings are worn or failing. Pump seal leaks are another clear sign, leading to coolant drips under your vehicle. Additionally, your engine may overheat unexpectedly due to reduced coolant circulation. You could notice a drop in heater performance or fluctuating temperature gauges. In conclusion, if the water pump belt shows cracks or looseness, it’s a sign the pump may soon fail. Keep an eye out for these signs to prevent engine overheating. Addressing water pump issues early can save you from costly repairs and prevent further damage to your engine. High critical acclaim and box office success can also indicate the importance of timely maintenance for related components.
Water Pump Replacement Tips
When replacing a faulty water pump, it’s essential to follow proper procedures to guarantee a reliable fix. Start by draining the coolant from the radiator and disconnecting the radiator cap to prevent pressure buildup. Next, locate the water pump, usually near the timing belt or serpentine belt, and remove any accessories blocking access. Before installing the new pump, check the coolant reservoir for contamination and flush it if necessary. When installing the new pump, ensure the gasket or seal is properly seated to prevent leaks. Reattach the serpentine belt and refill the cooling system with fresh coolant. Finally, tighten the radiator cap securely and run the engine to verify proper operation, watching for leaks or overheating signs. Proper attention guarantees your repair lasts. Additionally, being aware of common engine overheating causes can help you diagnose and prevent future issues effectively.
Damaged or Worn-Out Cooling Fans
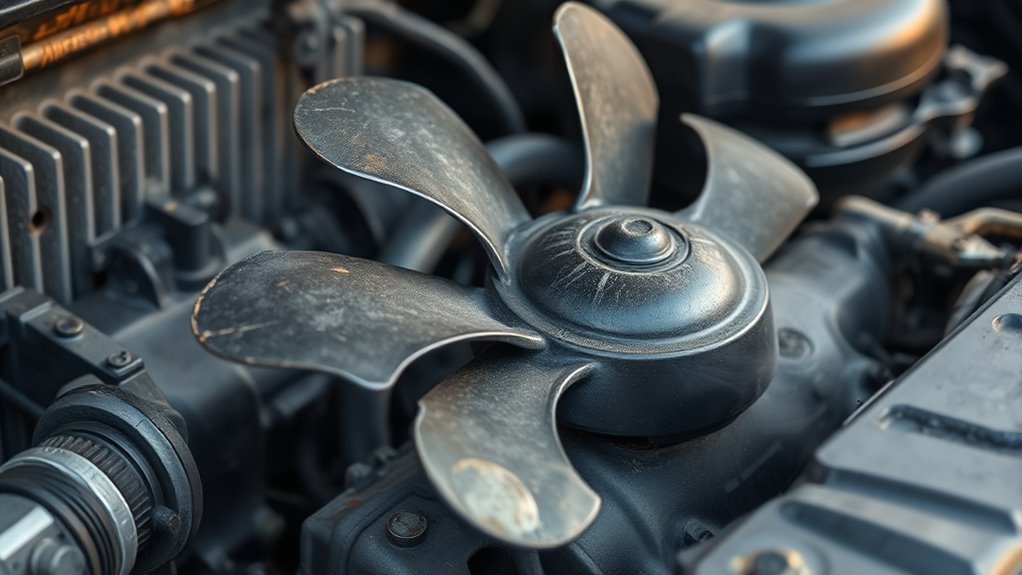
Damaged or worn-out cooling fans are a common culprit behind engine overheating. When cooling fan malfunctions occur, they often stem from fan blade damage or motor failure, reducing airflow and cooling efficiency. You might notice the fan isn’t spinning or making unusual noises. Over time, the blades can become cracked or bent, further impairing performance. Faulty wiring or a broken fan clutch can also hinder operation. These issues prevent proper heat dissipation, risking engine damage. To diagnose, check for visible fan damage, listen for abnormal sounds, and verify that the fan engages when the engine heats up. Addressing these problems promptly can prevent costly repairs and keep your engine running smoothly. Additionally, understanding the Mazda Tuning options can help improve cooling system performance and prevent overheating issues.
Broken or Loose Hoses
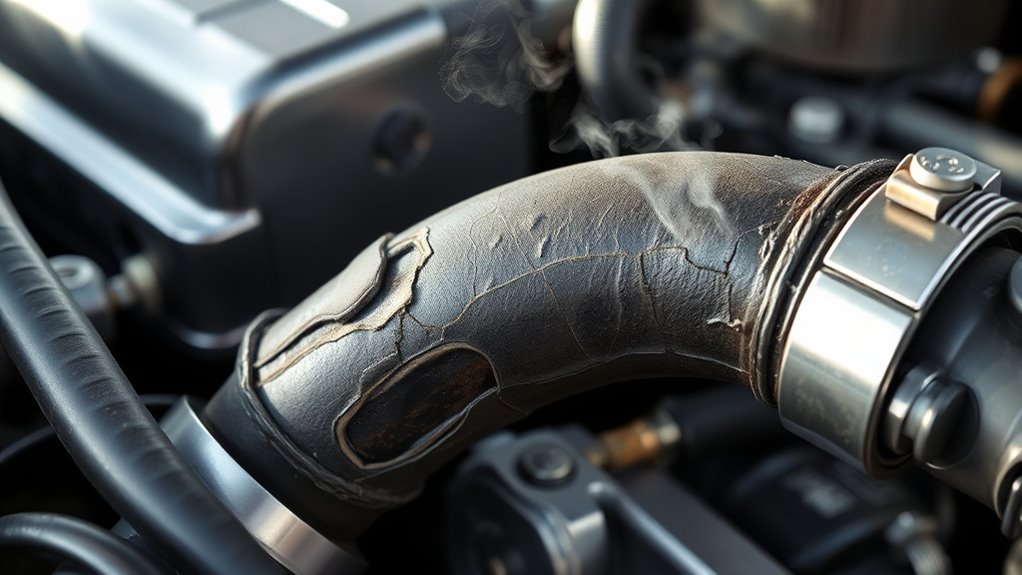

Broken or loose hoses can substantially contribute to engine overheating by disrupting the coolant flow. When hoses are damaged or their hose integrity is compromised, coolant leaks can occur, preventing proper circulation through the engine and radiator. Regularly check the condition of your hoses for cracks, bulges, or softness, which indicate deterioration. Ensuring clamp tightness is equally important; loose clamps can cause leaks at connection points, reducing coolant pressure and flow. If you notice any coolant loss or visible leaks around hoses, replace or tighten them immediately. Properly maintained hoses and secure clamps keep the cooling system sealed and functioning efficiently. Addressing these issues promptly helps prevent overheating caused by compromised coolant circulation. Routine appliance maintenance and inspections can help identify hose issues before they lead to engine damage.
Head Gasket Failures

Head gasket failures can cause engine overheating by allowing coolant to leak or bypass the combustion chamber. When the gasket fails, it compromises the seal between cylinders and cooling passages, leading to loss of engine compression issues and coolant leakage. This prevents proper heat transfer, causing the engine to overheat. You might notice white smoke from the exhaust, milky oil, or coolant loss without obvious leaks. Additionally, misfires and reduced power can signal head gasket problems. Proper inspection and repair are essential to prevent further engine damage.
Overworked Engine Components and Heavy Towing

When you tow heavy loads or push your engine beyond its normal limits, the engine components endure increased stress, raising the risk of overheating. Overworked parts like the radiator, cooling fan, and pistons must work harder, which can strain the engine’s design and compromise fuel efficiency. Heavy towing forces the engine to generate more heat, especially if it’s not built for such tasks. If your vehicle’s engine design isn’t optimized for heavy loads, it may struggle to dissipate heat effectively, leading to overheating. Additionally, constant overexertion can cause wear and tear, reducing fuel efficiency over time. To prevent this, ensure your engine is rated for towing and avoid pushing it beyond recommended limits, especially during long or steep climbs.
External Factors: Weather and Driving Conditions

External factors like weather and driving conditions can markedly influence your engine’s temperature, especially after overworking it with heavy towing or intense driving. High ambient temperatures increase the weather impact, making cooling more difficult. Hot, humid days reduce the efficiency of your radiator and cooling system. Additionally, driving on steep inclines or rough terrain strains your engine further, raising its temperature.
- Extreme heat can cause coolant to evaporate faster, leading to overheating
- Stop-and-go traffic increases engine strain and reduces airflow
- High humidity hampers heat dissipation from the engine
- Driving in hot weather amplifies the effects of cooling system wear
- Towing heavy loads in summer worsens the weather impact on engine temperature
Frequently Asked Questions
Can Engine Overheating Occur Without Visible Coolant Leaks?
Yes, engine overheating can happen without visible coolant leaks. Coolant evaporation can occur over time, reducing coolant levels without obvious signs. Hidden leaks might develop in hard-to-see areas like the radiator, hoses, or water pump, causing coolant loss that isn’t immediately visible. Regularly checking your coolant levels and inspecting for subtle signs of leaks can help prevent overheating and keep your engine running smoothly.
How Does Altitude Affect Engine Cooling Efficiency?
Surprisingly, altitude effects can turn your engine’s cooling system into a real challenge. As you ascend, the thinner air offers less cooling, making your engine work harder to stay cool. That’s right—those mountain drives can give you cooling challenges you didn’t expect. Keep an eye on temperature gauges, because altitude effects aren’t just a scenic route—they’re a test for your engine’s cooling efficiency. Stay vigilant!
Are Electrical Issues a Common Cause of Overheating?
Electrical issues, like faults or wiring problems, can definitely cause engine overheating. When electrical faults disrupt cooling fans or sensor functions, your engine might not get proper airflow or temperature regulation. Wiring issues can also lead to short circuits or power failures in critical cooling components. So, if your engine is overheating, it’s worth checking the electrical system. Faulty wiring or electrical faults could be the hidden culprits behind the temperature rise.
Can a Clogged Air Filter Contribute to Engine Overheating?
Think of your engine as a vintage radio; a clogged air filter is like a blocked antenna. When your air filter gets dirty, it restricts airflow, making it harder for your engine to cool properly. This hampers engine cooling and can lead to overheating. So, yes, a clogged air filter plays a significant role in overheating, emphasizing the importance of regular maintenance to keep your engine running smoothly and prevent breakdowns.
How Does Engine Age Influence Overheating Risk?
Your engine’s age directly impacts overheating risk because, over time, engine lifespan is affected by wear and tear. As your engine gets older, components like the cooling system and seals may weaken, reducing efficiency. This increases the chance of overheating, especially if regular maintenance is neglected. Keep an eye on signs of aging and guarantee timely repairs to prevent overheating issues caused by the natural decline in engine performance.
Conclusion
Did you know that engine overheating causes about 40% of all vehicle breakdowns? Staying alert to issues like coolant leaks, faulty thermostats, or damaged fans can save you from costly repairs and roadside mishaps. Regular maintenance checks are your best defense against overheating. By understanding these common causes, you can keep your engine running smoothly and avoid unexpected breakdowns, ensuring safer and more reliable driving every time.









